《深入理解 C++ 中的 IO 流【iostream篇】》
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_63050691/article/details/137053406
C++ 中的输入输出流(iostream)是非常重要的一部分,它们提供了与用户交互以及与文件系统进行数据交换的功能。
本文将深入探讨 C++ 中的 cin 和 cout,介绍它们的使用方法、缓冲区以及常用的成员函数等相关知识。
1. cin 和 cout 的基本使用
在 C++ 中,cin 和 cout 是标准输入输出流对象,分别用于从标准输入(通常是键盘)读取数据和向标准输出(通常是屏幕)写入数据。
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int num;
std::cin >> num;
std::cout << num << std::endl;
return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,我们使用 cout 来打印提示消息,并使用 cin 读取用户输入的数字。
2. 运算符重载与 iostream
在 iostream 中,常见的运算符重载包括插入运算符 << 和提取运算符 >>。这两个运算符分别用于输出数据到流和从流中提取数据。
重载插入运算符 <<
插入运算符 << 用于将数据插入到输出流中,通常用于输出数据到控制台或文件。
#include <iostream>
class MyClass {
public:
int data;
MyClass(int d) : data(d) {}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const MyClass& obj) {
os << obj.data;
return os;
}
};
int main() {
MyClass obj(10);
std::cout << obj << std::endl;
return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,我们重载了 << 运算符,使得 MyClass 类型的对象可以直接通过 cout 输出。
重载提取运算符 >>
提取运算符 >> 用于从输入流中提取数据,通常用于从控制台或文件中读取数据。
#include <iostream>
class MyClass {
public:
int data;
MyClass() {}
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, MyClass& obj) {
is >> obj.data;
return is;
}
};
int main() {
MyClass obj;
std::cin >> obj;
std::cout << obj.data << std::endl;
return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,我们重载了 >> 运算符,使得可以直接从 cin 输入到 MyClass 类型的对象。并且由于fstream和sstream继承了iostream,因此重载了iostream后fstream和sstream也可以使用。
3. cin 和 cout 的缓冲区
在默认情况下,cin 和 cout 都是带有缓冲区的。这意味着输入的数据不会立即被程序处理,而是暂时存储在缓冲区中,直到程序需要时才进行读取或写入操作。
缓冲区刷新
缓冲区的刷新通常由以下情况触发:
- 缓冲区已满:当缓冲区填满数据时,会自动刷新缓冲区,将数据发送给目标设备(如屏幕)。
- 手动刷新:可以使用 std::flush 强制刷新输出缓冲区。
std::cout << "Flushing buffer" << std::flush;
flush (以水)冲刷,冲洗
buffer 缓冲区
关闭缓冲区
有时候,我们可能需要关闭缓冲区以实时地输出数据,而不需要等到缓冲区满或程序结束时才输出。可以使用 std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false) 来关闭 cin 和 cout 的缓冲区。
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 关闭缓冲区
std::cout << "This will be printed immediately" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
4. cin 和 cout 的常用成员函数
cin 和 cout 提供了许多有用的成员函数,可以帮助我们更灵活地处理输入输出操作。
cin 成员函数
- cin.get(): 从输入流中获取下一个字符。
- cin.getline(char*, int): 从输入流中获取一行数据。可指定分割符,默认为’\n’。
- cin.read(char*, int):从输入流中读取一定数量的字符
cout 成员函数
- cout.put(char): 向输出流中写入一个字符。
- cout.write(char*, int): 向输出流中写入一定数量的字符。
《C++: I/O流详解》
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/llxblogs/p/7768353.html
一、输入流操作
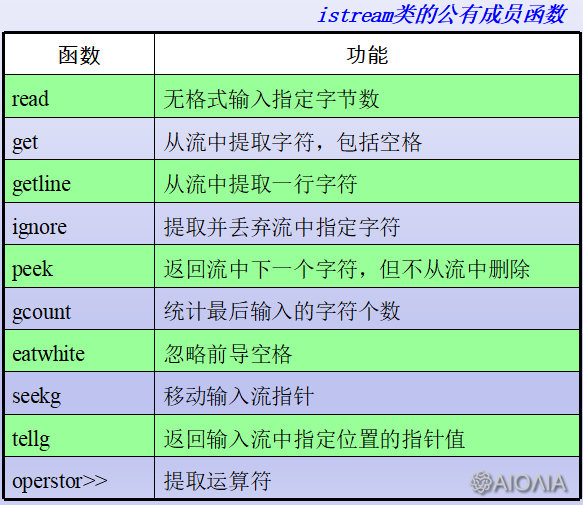
1. read 无格式输入指定字节数
istream& read ( char* pch, int nCount );
istream& read ( unsigned char* puch, int nCount );
istream& read ( signed char* psch, int nCount );
2. get 从流中提取字符,包括空格
int get();
istream& get( char* pch, int nCount, char delim = ‘\n’ );
istream& get( unsigned char* puch, int nCount, char delim = ‘\n’ );
istream& get( signed char* psch, int nCount, char delim = ‘\n’ );
istream& get( char& rch ); istream& get( unsigned char& ruch );
istream& get( signed char& rsch );
istream& get( streambuf& rsb, char delim = ‘\n’ );
3. getline 从流中提取一行字符
istream& getline( char* pch, int nCount, char delim = ‘\n’ );
istream& getline( unsigned char* puch, int nCount, char delim = ‘\n’ );
istream& getline( signed char* psch, int nCount, char delim = ‘\n’ );
4. ignore 提取并丢弃流中指定字符
istream& ignore( int nCount = 1, int delim = EOF );
5. peek 返回流中下一个字符,但不从流中删除
int peek();
6. gcount 统计最后输入的字符个数
int gcount() const;
7. eatwhite 忽略前导空格
void eatwhite();
8. seekg 移动输入流指针
istream& seekg( streampos pos );
istream& seekg( streamoff off, ios::seek_dir dir );
9. tellg 返回输入流中指定位置的指针值
streanpos tellg();
10. operator >> 提取运算符
basic_istream& operator>>( basic_istream& (*pf)(basic_istream&));
basic_istream& operator>>( basic_ios<E, T>& (*pf)(basic_ios<E, T>&));
basic_istream& operator>>( ios_base<E, T>& (*pf)(ios_base<E, T>&));
basic_istream& operator>>( basic_streambuf<E, T> *sb);
basic_istream& operator>>(bool& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(short& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(unsigned short& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(int& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(unsigned int& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(long& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(unsigned long& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(void *& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(float& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(double& n);
basic_istream& operator>>(long double& n);
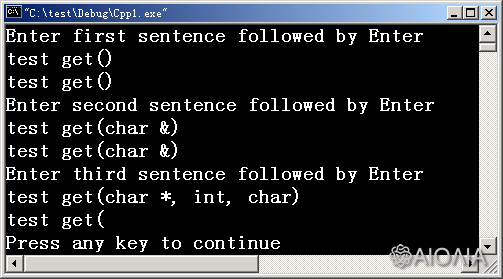
例子:
//用get函数从键盘输入字符
void f1(){
char c;
cout<<"Enter first sentence followed by enter\n";
while((c = cin.get())!='\n')
cout.put(c);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"Enter second sentence followed by enter\n";
while(cin.get(c)){
if (c == '\n')
break;
cout.put(c);
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"Enter thired sentence followed by enter\n";
char s[80];
cin.get(s, 10);
cout<<s<<endl;
}
输出:
二、输出流
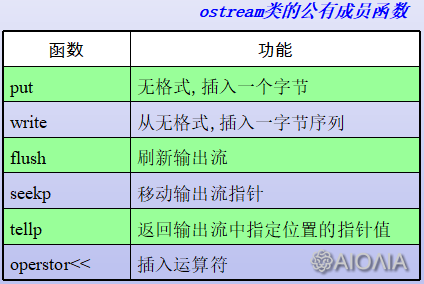
1. put 无格式,插入一个字节
ostream& put(char ch);
2. write 从无格式,插入一字节序列
ostream& write( const char* pch, int nCount );
ostream& write( const unsigned char* puch, int nCount );
ostream& write( const signed char* psch, int nCount );
3. flush 刷新输出流
ostream& flush();
4. seekp 移动输出流指针
ostream& seekp( streampos pos );
ostream& seekp( streamoff off, ios::seek_dir dir );
5. tellp 返回输出流中指定位置的指针
streampos tellp();
6. operstor<< 插入运算符
basic_ostream& operator<<( basic_ostream& (*pf)(basic_ostream&));
basic_ostream& operator<<( basic_ios<E, T>& (*pf)(basic_ios<E, T>&));
basic_ostream& operator<<( ios_base<E, T>& (*pf)(ios_base<E, T>&));
basic_ostream& operator<<( basic_streambuf<E, T> *sb);
basic_ostream& operator<<(const char *s);
basic_ostream& operator<<(char c);
basic_ostream& operator<<(bool n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(short n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(unsigned short n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(int n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(unsigned int n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(long n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(unsigned long n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(float n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(double n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(long double n);
basic_ostream& operator<<(void *n);
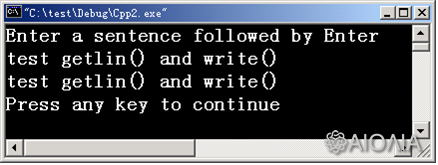
例子:
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{ cout << "Enter a sentence followed by Enter\n" ;
char s[ 26 ] ;
cin.getline ( s, 26 ) ;
cout.write(s, 26) ;
cout<<endl;
}
输出:
三、流错误状态
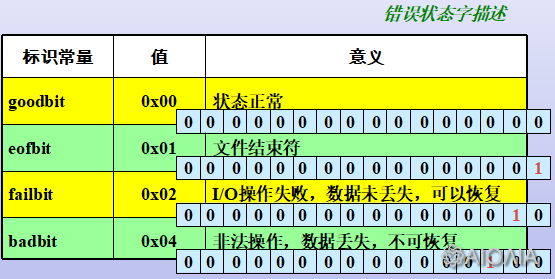
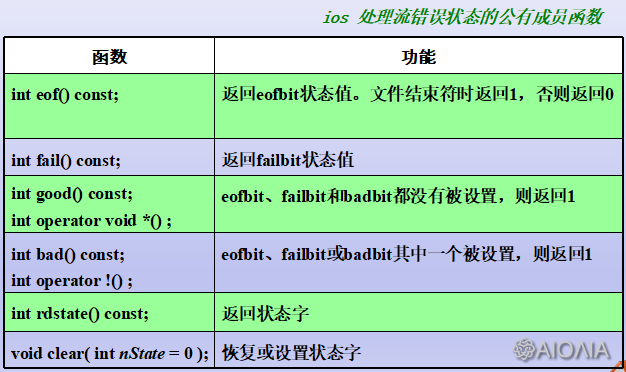
《C++: I/O流详解(二)——输入输出格式控制》
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/llxblogs/p/7768669.html
一、格式控制
ios提供直接设置标志字的控制格式函数
iostream和iomanip库还提供了一批控制符简化I/O格式化操作
状态标志 值 含义 输入/输出 skipws 0X0001 跳过输入中的空白 I left 0X0002 左对齐输出 O right 0X0004 右对齐输出 O internal 0X0008 在符号位和基指示符后填入字符 O dec 0X0010 转换基制为十进制 I/O oct 0X0020 转换基制为八进制 I/O hex 0X0040 转换基制为十六进制 I/O showbase 0X0080 在输出中显示基指示符 O showpoint 0X0100 输出时显示小数点 O uppercase 0X0200 十六进制输出时一律用大写字母 O showpos 0X0400 正整数前加“+”号 O scientific 0X0800 科学示数法显示浮点数 O fixed 0X1000 定点形式显示浮点数 O unitbuf 0X2000 输出操作后立即刷新流 O stdio 0X4000 输出操作后刷新stdout 和 stdree O
设置标识字:
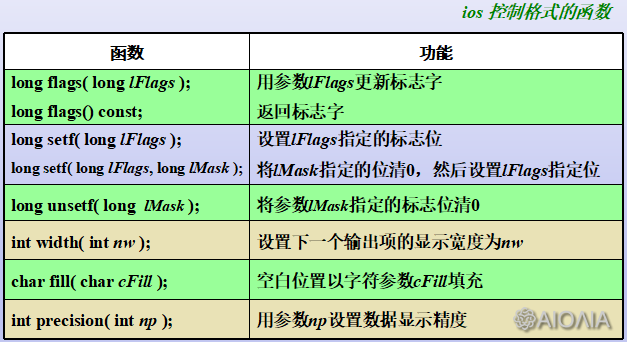
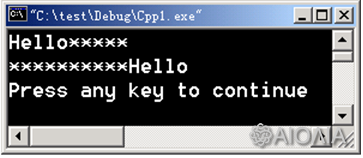
例1:
//例10-4 设置输出宽度
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{ char *s = "Hello";
cout.fill( '*' ) ; // 置填充符
cout.width( 10 ) ; // 置输出宽度
cout.setf( ios :: left ) ; // 左对齐
cout << s << endl ;
cout.width( 15 ) ; // 置输出宽度
cout.setf( ios :: right, ios :: left ) ; // 清除左对齐标志位,置右对齐
cout << s << endl ;
}
输出:
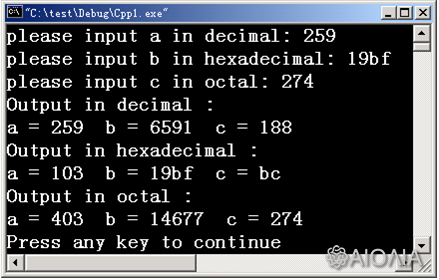
例二:不同基数形式的输入输出
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{ int a , b , c ;
cout << "please input a in decimal: " ;
cin.setf( ios :: dec , ios :: basefield ) ; cin >> a ; //十进制输入
cout << "please input b in hexadecimal: " ;
cin.setf( ios :: hex , ios :: basefield ) ; cin >> b ; //十六进制输入
cout << "please input c in octal: " ;
cin.setf( ios :: oct , ios :: basefield ) ; cin >> c ; //八进制输入
cout << "Output in decimal :\n" ;
cout.setf( ios :: dec, ios :: basefield ); //十进制输出
cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << " c = " << c << endl ;
cout.setf( ios :: hex , ios :: basefield ) ; //十六进制输出
cout << "Output in hexadecimal :\n" ;
cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << " c = " << c << endl ;
cout.setf( ios :: oct , ios :: basefield ) ; //八进制输出
cout << "Output in octal :\n" ;
cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << " c = " << c << endl ;
}
输出:
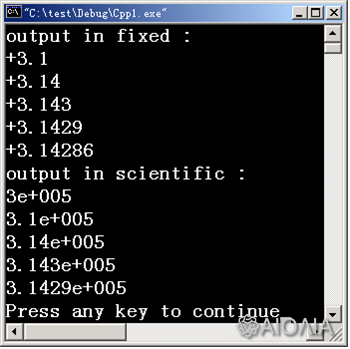
例三:格式化输出浮点数
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{ double x = 22.0/7 ;
int i ;
cout << "output in fixed :\n" ;
cout.setf( ios::fixed | ios::showpos ) ; // 定点输出,显示 +
for( i=1; i<=5; i++ )
{ cout.precision( i ) ; cout << x << endl ; }
cout << "output in scientific :\n" ;
// 清除原有设置,科学示数法输出
cout.setf(ios::scientific, ios::fixed|ios::showpos ) ;
for( i=1; i<=5; i++ )
{ cout.precision(i) ; cout << x*1e5 << endl ; }
}
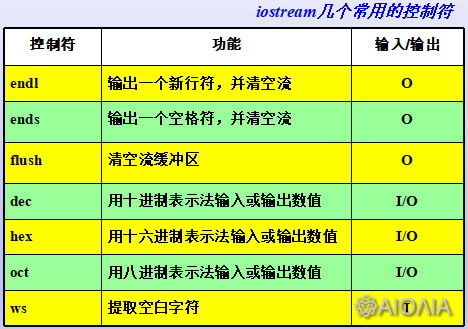
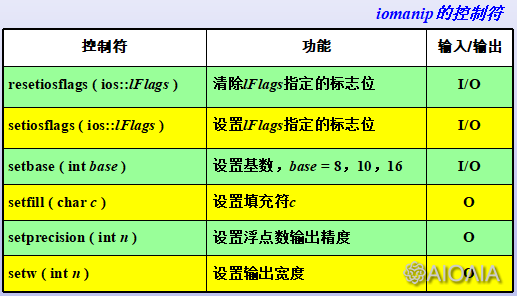
二、格式控制符
控制符是istream和ostream类定义了一批函数,作为重载插入运算符<<或提取运算符>>的右操作数控制I/O格式。
例1:
// 整数的格式化输出
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std ;
void main()
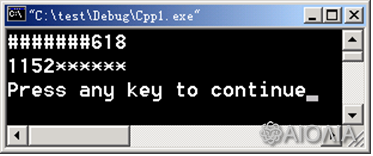
{ const int k = 618 ;
cout << setw(10) << setfill('#') << setiosflags(ios::right) << k <<endl ;
cout << setw(10) << setbase(8) << setfill('*')
<< resetiosflags(ios::right) << setiosflags(ios::left) << k << endl ;
}
输出:
《C++: I/O流详解(三)——串流》
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/llxblogs/p/7768786.html
一、串流
串流类是 ios 中的派生类
C++的串流对象可以连接string对象或字符串
串流提取数据时对字符串按变量类型解释;插入数据时把类型 数据转换成字符串
串流I/O具有格式化功能
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <strstream>
using namespace std;
//?什么鬼?
/*从输入串流对象提取数据
int main(){
string testStr("Input test 256*0.5");
string s1, s2, s3;
double x, y;
istringstream input(testStr); //用string对象构造串流对象
input>> s1>> s2>> x>> s3>> y;
cout<< s1<< ends<< s2<< ends<< x<< s3<< y<< "="<< x*y<< endl;
return 0;
}
*/
//向输出串流对象插入数据
/*
int main(){
ostringstream Output;
double x, y;
cout<< "Input x:";
cin>> x;
cout<< "Input y:";
cin>> y;
Output<<x<<"*"<<y<<"="<<x*y<<endl;
cout<<Output.str();
return 0;
}
*/
//向输出串流对象插入数据
int main(){
char buf[80];
ostrstream Output(buf, sizeof(buf));//对Output的数据成员初始化
double x, y;
cout<< "Input x:";
cin>> x;
cout<< "Input y:";
cin>> y;
Output<<x<<"*"<<y<<"="<<x*y<<endl;
cout<<Output.str();
return 0;
}